
Introduction
Navigating the universe of insurance can appear daunting, even more when you introduce a subcategory known as reinsurance. Unlike the typical insurance that you’re probably more familiar with, reinsurance operates behind the scenes, effectively invisible to the everyday policyholder.
Understanding the basics of insurance and reinsurance
Insurances main role is to mitigate a specific risk, providing financial reimbursement to the policyholder if the worst-case scenario occurs. However, what happens if the financial impact of a catastrophe is too significant for the insurance company to manage alone? That’s where reinsurance comes into play. It is a form of ‘insurance for insurers’, designed to protect insurance companies from severe financial strain by redistributing risk across multiple parties. This behind-the-scenes protection not only strengthens the insurance company’s financial standing but also ensures policyholders are covered, even in the face of potentially ruinous events.
The Importance of Reinsurance
The robust world of insurance doesn’t function independently; reinsurance forms an integral part of it. As the backbone of the insurance industry, reinsurance creates a safety net for insurance companies, enabling them to stay afloat amidst claims, especially during catastrophic events.
Risk mitigation and financial stability
Reinsurance serves as a practical tool for mitigating risks. It enables companies to transfer excessive risks, preventing them from getting swallowed up by large claims. This arrangement plays a crucial role in maintaining financial stability within the insurance entity.
The role of reinsurance in protecting insurance companies
Moreover, reinsurance functions as a protective cover for insurance companies. Similar to how policyholders rely on insurance to cushion against unforeseen events, insurance companies rely on reinsurance. It limits their exposure to a loss, ensuring that they aren’t financially crippled by colossal payouts. By insulating insurers from significant losses, reinsurance ensures the continued operation of insurance companies, ultimately securing policyholders’ interests.
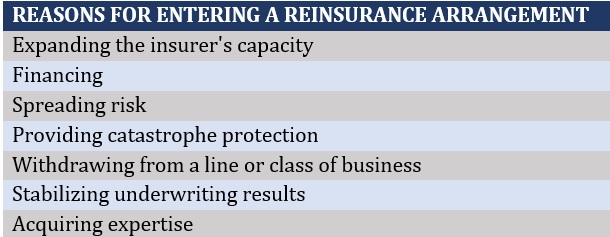
Types of Reinsurance
In the unpredictable world of risks and potential losses, reinsurance comes as quite the safety net serving as an insurance for the insurers themselves. It comes in many forms, so let’s pinpoint a few.
Treaty reinsurance and facultative reinsurance
Treaty reinsurance means the reinsurer must accept all risks that an insurer needs to pass on. Conversely, facultative reinsurance gives the reinsurer the ability to accept or deny individual risks.
Proportional and non-proportional reinsurance
Proportional reinsurance refers to situations where the reinsurer shares the same proportion of risks and premiums of the insurer. In contrast, non-proportional reinsurance fixes the level of risk the reinsurer must take on, regardless of the size of the original loss. This clear understanding of reinsurance types paves the way for a safer insurance market for all.
Benefits of Reinsurance
In the dynamic and often complex world of insurance, reinsurance serves as a pivotal mechanism that safeguards insurers against excessive losses. It brings about countless benefits in terms of both operational flexibility and risk management.
Increasing capacity and underwriting flexibility
One of the key roles of reinsurance is expanding companies’ capacity for taking on more risks, hence enabling a greater degree of underwriting flexibility. This empowerment in turn paves the way for better growth prospects, especially for newer insurance firms still finding their footing.
Managing catastrophic risks and reducing volatility
Furthermore, reinsurance majors on mitigating catastrophic risks. It does so by transferring a portion of the insurer’s liability, providing a shock absorber during catastrophic events. As a result, the drastic impact of significant losses is cushioned and financial stability sustained. Concurrently, reinsurance also smoothens earnings by reducing volatility arising from large claim fluctuations. Consequently, reinsuring is not just a mere option but a strategic move for any modern insurance company.
Challenges in Reinsurance
Today’s everchanging insurance landscape calls for better risk management. This is where reinsurance becomes pivotal. But, implementing reinsurance is not without its set of challenges.
Pricing and underwriting challenges
Reinsurance often poses significant pricing and underwriting issues. Accurately pricing risks is challenging due to the lack of historical data for certain risks. There’s also a need for sophisticated underwriting skills to assess complex risks appropriately.
Regulatory and legal considerations
Regulatory and legal aspects present another layer of complication. Regulatory requirements differ across countries, making international reinsurance complex. Plus, constant changes in regulatory standards mean reinsurers must stay up-to-date or risk non-compliance. Legal considerations in contract interpretation can also lead to disputes. Successful reinsurance requires navigating these intricate dynamics.


