Introduction
The global insurance industry was a robust sector before the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Overview of the global insurance industry before COVID-19
The industry was characterized by steady growth, with insurers worldwide enjoying increased premiums and profitability. However, the outbreak of COVID-19 has significantly disrupted this trajectory, causing a ripple effect on the global insurance landscape. The pandemic has brought about unprecedented challenges, leading to a major shift in how insurers operate and interact with their clients.
COVID-19 and the Insurance Industry
The COVID-19 pandemic has hit industries worldwide, and the insurance sector is no exception.
The immediate impact of the pandemic on insurance companies
The most immediate impact of the pandemic on insurance companies has been a surge in claims, particularly in health and travel insurance. Simultaneously, life insurers faced a rise in mortality rates, leading to increased payouts. However, on the flip side, lockdown measures led to fewer auto insurance claims due to less road traffic. The pandemic has indeed reshaped the landscape of the global insurance industry.
Changes in Customer Behavior
The global insurance industry has experienced a significant shift due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Shifts in insurance purchasing patterns and demands
COVID-19 has altered consumer behavior, leading to changes in insurance purchasing patterns. The demand for health and life insurance policies has skyrocketed, while the need for travel insurance has plummeted. The pandemic has also triggered a surge in digital interactions, pushing insurers to enhance their online platforms and services.
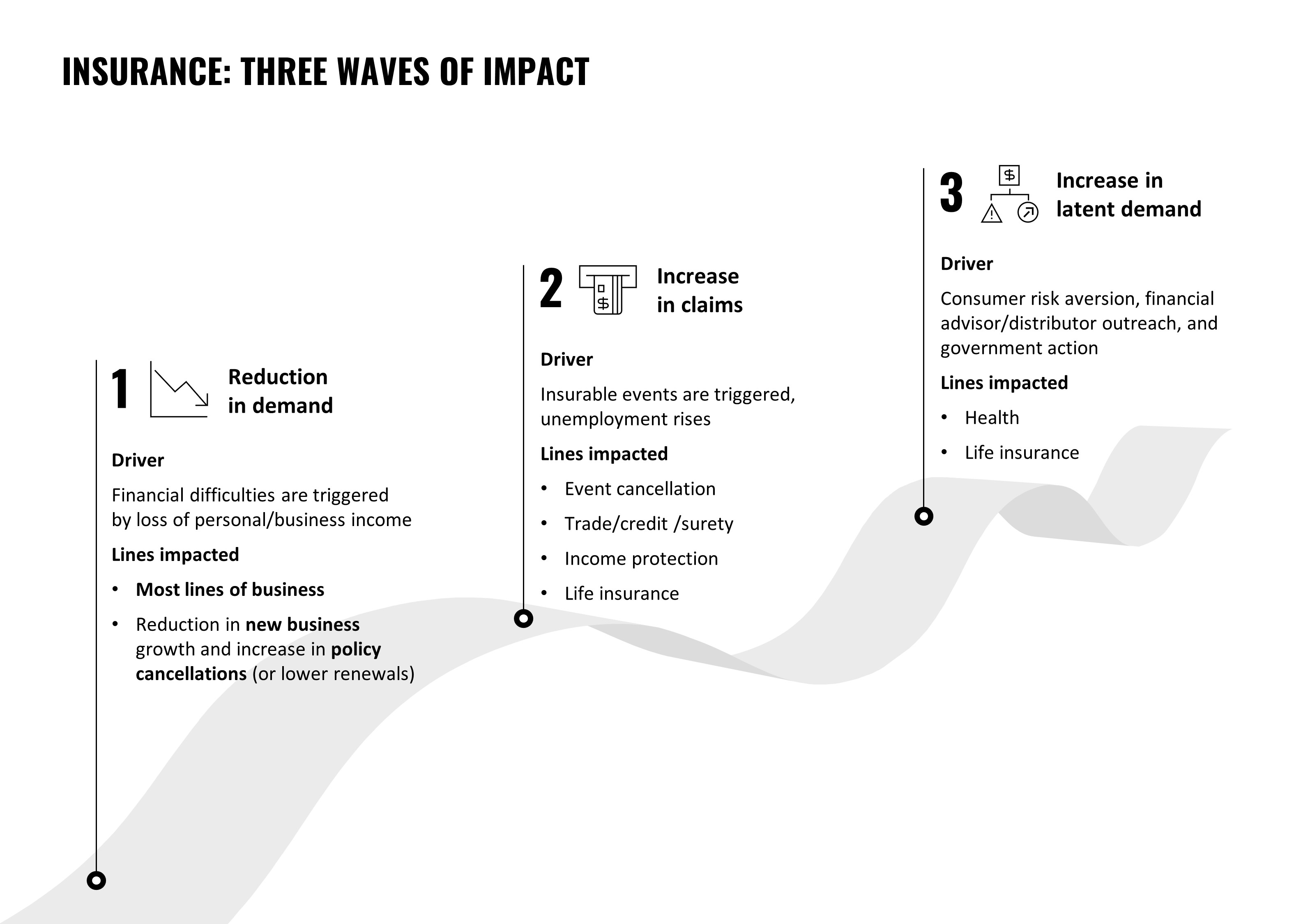
Financial Losses and Claims
The global insurance industry has been hit hard by the COVID-19 pandemic. The unprecedented crisis has led to a significant increase in insurance claims, causing financial losses for companies. The insurance industry has been grappling with the challenges of increased claims, especially in sectors like health, travel, and business interruption insurance. This surge in claims has put immense pressure on insurers, leading to substantial financial losses.
The global insurance industry has experienced significant impacts due to the COVID-19 pandemic. One major effect has been the disruption of business operations for insurance companies around the world.
How COVID-19 has affected the day-to-day operations of insurance companies
- Remote Work: Insurance companies have had to quickly adapt to remote work arrangements to ensure the safety of their employees. This shift has required the implementation of new technologies and communication tools to maintain productivity and collaboration.
- Claims Processing: The pandemic has led to an increase in insurance claims, particularly in areas such as travel and health insurance. Insurance companies have had to handle a surge in claims while also dealing with challenges such as limited staff availability and delays in claim processing.
- Risk Assessment: COVID-19 has introduced new risks and uncertainties for insurers. They have had to reassess their risk models and underwriting processes to account for the impact of the pandemic on various industries and sectors.
- Customer Service: Insurance companies have faced challenges in providing seamless customer service during these unprecedented times. With office closures and limited staff, response times may have been affected, leading to potential customer dissatisfaction.
- Financial Impact: The economic downturn caused by the pandemic has had financial implications for insurance companies. Investment portfolios may have been negatively impacted, leading to potential losses and reduced profitability.
Overall, the COVID-19 pandemic has forced insurance companies to adapt quickly and find innovative solutions to continue serving their customers while navigating the challenges posed by the global health crisis.
Digital Transformation
Accelerated adoption of digital tools and technologies in the insurance industry
The global insurance industry has experienced a major impact due to the COVID-19 pandemic. One significant outcome has been the accelerated adoption of digital tools and technologies. Insurance companies have quickly shifted to remote work setups, online customer interactions, and digital claims processing. This transformation has not only enabled insurers to continue their operations during lockdowns but has also improved efficiency and customer experience. With the increased reliance on digital platforms, insurers are now embracing innovative technologies such as artificial intelligence, data analytics, and blockchain to streamline processes and enhance risk assessment. The pandemic has acted as a catalyst for the industry’s digital transformation, pushing insurers to embrace technology and adapt to the changing landscape. This shift towards digitization is expected to have long-term benefits for the insurance industry, including improved operational resilience, cost savings, and enhanced customer engagement. As the world recovers from the pandemic, it is likely that digital transformation will continue to shape the future of the global insurance industry.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a major impact on the global insurance industry, leading to significant changes in regulations and government support. Regulators and governments have responded swiftly to address the challenges faced by insurers during these unprecedented times.
The response of regulators and governments to support the insurance industry
- Regulatory flexibility: Regulators around the world have implemented measures to provide flexibility to insurers in terms of compliance requirements and reporting deadlines. This has allowed insurers to focus on managing the impact of the pandemic on their operations and customers.
- Government support: Many governments have introduced stimulus packages and financial assistance programs to support businesses, including insurance companies. These measures aim to ensure the stability of the insurance sector and protect policyholders.
- Enhanced consumer protection: Regulators have also taken steps to enhance consumer protection during this crisis. They have issued guidelines on fair treatment of policyholders, extended grace periods for premium payments, and encouraged insurers to provide coverage for COVID-19-related claims.
- Increased digitalization: The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital technologies in the insurance industry. Insurers are leveraging digital platforms for policy sales, claims processing, and customer service, enabling them to continue operations remotely and meet customer needs effectively.
- Risk assessment and management: Insurers are reevaluating their risk models and underwriting practices in light of the pandemic. This includes assessing the potential impact of future pandemics or similar events on their business continuity plans.
The regulatory challenges and government support in response to COVID-19 have played a crucial role in helping the insurance industry navigate through these uncertain times and ensure its resilience in the face of future challenges.
Future Outlook and Adaptation Strategies
Predictions and strategies for the insurance industry post-COVID-19
The global insurance industry has been significantly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. Here are some key points to consider:
- Increased demand for certain insurance products: The pandemic has highlighted the importance of health, life, and business interruption insurance. As a result, there is expected to be a surge in demand for these types of coverage.
- Shift towards digitalization: The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital technologies in the insurance industry. Insurers are investing in online platforms, digital claims processing, and virtual customer interactions to enhance efficiency and customer experience.
- Risk assessment and pricing: Insurers will need to reassess their risk models and pricing strategies in light of the new risks posed by pandemics. This may lead to changes in premiums and coverage options.
- Remote work and cybersecurity: The shift to remote work has increased the vulnerability of insurance companies to cyber threats. Insurers will need to strengthen their cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive customer data.
- Collaboration with insurtech startups: Insurers are partnering with insurtech startups to leverage their innovative technologies and improve operational efficiency. This collaboration can lead to faster claims processing, personalized policies, and improved customer engagement.
- Focus on customer-centricity: The pandemic has highlighted the importance of putting customers at the center of insurance operations. Insurers will need to provide flexible policies, empathetic customer service, and seamless digital experiences to meet evolving customer expectations.
In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic has brought about significant changes in the global insurance industry. Insurers must adapt by embracing digitalization, reassessing risk models, strengthening cybersecurity, collaborating with insurtech startups, and prioritizing customer-centricity to thrive in the post-pandemic world.
Conclusion
Summary of the major impacts of COVID-19 on the global insurance industry
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the global insurance industry. Here are the key points to note:
- Increased claims: The pandemic has led to a surge in insurance claims, particularly in areas such as travel, health, and business interruption insurance.
- Financial strain: Insurance companies have faced financial challenges due to increased payouts and reduced premium income. This has resulted in a need for cost-cutting measures and potential premium increases.
- Shift in risk perception: The pandemic has highlighted the importance of risk management and insurance coverage. Individuals and businesses are now more aware of the need for comprehensive insurance policies.
- Digital transformation: The insurance industry has accelerated its digital transformation efforts to adapt to remote work, online customer interactions, and streamlined claims processes.
- New product offerings: Insurance companies have introduced new products to address emerging risks related to the pandemic, such as pandemic-specific coverage and parametric insurance.
- Regulatory changes: Governments and regulatory bodies have implemented new guidelines and regulations to address the challenges posed by the pandemic, including coverage requirements and consumer protection measures.
- Long-term implications: The full impact of COVID-19 on the insurance industry is still unfolding. It is likely to reshape the industry’s landscape, driving innovation, and changing customer expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How has COVID-19 affected insurance claims?
The pandemic has led to an increase in insurance claims, particularly in areas such as travel, health, and business interruption insurance. - Are insurance companies financially impacted by COVID-19?
Yes, insurance companies have faced financial challenges due to increased payouts and reduced premium income. This has resulted in cost-cutting measures and potential premium increases. - How has the pandemic influenced the insurance industry’s digital transformation?The pandemic has accelerated the insurance industry’s digital transformation efforts, leading to remote work, online customer interactions, and streamlined claims processes.
- What new insurance products have emerged due to COVID-19?Insurance companies have introduced new products to address emerging risks related to the pandemic, such as pandemic-specific coverage and parametric insurance.
- Are there any regulatory changes in response to COVID-19?Governments and regulatory bodies have implemented new guidelines and regulations to address the challenges posed by the pandemic, including coverage requirements and consumer protection measures.














